Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous tumors that grow within uterine muscle tissue and are the most common tumor within the female reproductive system. As a result, all women are at potential risk of developing fibroids, with a majority of cases diagnosed in women between the ages of 35 and 54.
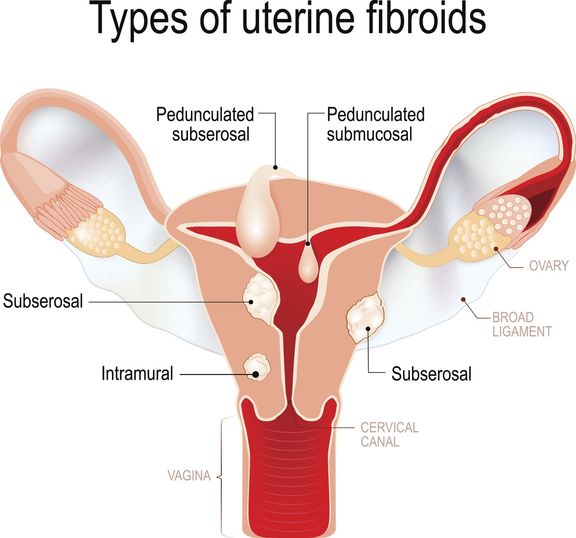
There are 4 types of uterine fibroids:
- Intramural fibroids — this is the most common type of fibroid, which develops within the uterine wall
- Subserosal fibroids — fibroids that develop on the outer uterine wall and can continue to grow outward in size
- Submucosal fibroids — the least common type of fibroid, develops under the lining of the uterine cavity
- Pedunculated fibroids — these tumors grow on a stalk, either into the uterus or outside on the uterine wall
Women may have one or multiple of these types of fibroids, which can make it challenging to determine which fibroid is causing symptoms.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids include excessive menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain and pressure, frequent urination and anemia. Many women can live a good quality of life with fibroids, some without any symptoms at all.
However, women diagnosed with fibroids by their OB/GYN physician, who experience symptoms that impact their lives and make daily tasks difficult, may be good candidates for a procedure called uterine fibroid embolization or UFE.
What is Uterine Fibroid Embolization?
Uterine fibroid embolization is a minimally invasive procedure used to alleviate symptoms of uterine fibroids and is an alternative option to removal of individual fibroids (myomectomy) or the entire uterus (hysterectomy). An interventional radiologist (IR) performs the procedure which takes about two hours. During the procedure, the IR makes a small skin nick in the groin or wrist to get access to the arteries feeding the fibroids.
At this point, the IR uses a specialized X‑ray to guide a small catheter into the arteries of the uterus. Small particles, about the size of grains of sand, are then injected into the artery supplying blood to the tumor. These particles will cut off the blood flow to the fibroid and cause it to shrink.
Uterine fibroid embolization is typically performed on an outpatient basis with average recovery time of one week, much shorter than other more invasive procedures that require a hospital stay. It’s also a very effective procedure with an approximate 90 percent success rate. A vast majority of women who have this procedure experience improvement in their symptoms and decrease in the size of the fibroids, allowing them to get back to enjoying normal daily activity.
If you’re experiencing symptoms or have been diagnosed with uterine fibroids, please call our Interventional Radiology department at 708−406−3328 or make an online appointment to schedule a consultation.
Health Topics:







