Obesity is a chronic, neurobehavioral disease that affects your health and can significantly reduce your overall quality of life. You are considered obese if your Body Mass Index (BMI) score, which compares your height to weight ratio, is 30 or higher. Over time, being overweight increases your risk of developing several other medical conditions. Bariatric surgeon, Jihad Kudsi, MD, shares some of the most common health risks associated with obesity.

According to the U.S. Surgeon General, obesity is a serious condition that can increase your risk of developing other health conditions including:
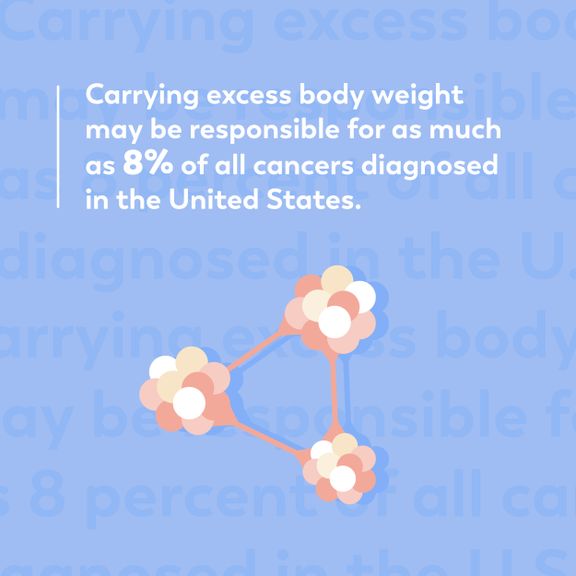
Certain cancers
According to the American Cancer Society (ACS), being overweight can increase your risk of developing several types of cancer, including those of the breast, colon, kidney or prostate. The link between your weight and cancer risk is still being studied, but is thought to be associated with increased inflammation in your body, the impact additional weight has on certain hormone levels and other factors that regulate cell growth.

Excessive Weight
Excess weight, especially if carried in your abdominal area, combined with a lack of physical activity can lead to insulin resistance. Often, following a healthy diet, getting regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can help eliminate the need for diabetic medications. Weight loss and long-term weight management can improve, and in some cases, resolve type 2 diabetes.

Hypertension
When there is additional fat tissue present, your body (and heart) has to work harder to pump blood throughout your body, adding pressure on your arteries and increasing your blood pressure. Over time, this can damage or weaken your heart and lead to other more serious heart related issues, like congestive heart failure.

Arrhythmia
Obesity can cause irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) or atherosclerosis (hardening of your arteries). This is because, over time, fat deposits build up in your arteries, restricting the flow of blood to your heart and cause blood clots to form. Having an arrhythmia increases your risk for cardiac arrest, a heart attack or stroke.

Sleep Apnea
Being overweight or obese often reduces your lung capacity, as fat accumulates in your neck, blocking your airflow and increasing your chances of developing respiratory infections, asthma or developing obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep apnea can also lead to additional weight gain because reduced sleep disrupts the production of hormones linked to your appetite and can cause you to feel drowsy and less active.
Our Weight Loss Clinic offers a variety of treatment options and the resources needed to achieve your weight loss goals and live a healthy, active lifestyle — from nutrition therapy and exercise planning to the management of metabolic disorders and surgical options. To schedule an appointment with the Weight Loss Clinic, call 630−348−3840.
If you are unable to achieve or maintain a healthy weight using diet and lifestyle modifications, you may want to consider additional treatment options, including bariatric (weight loss) surgery. In addition to being one of the most effective, long-lasting ways to treat obesity, bariatric surgery provides health benefits that go well beyond weight loss.
Learn more about the health benefits of bariatric surgery.
Health Topics: